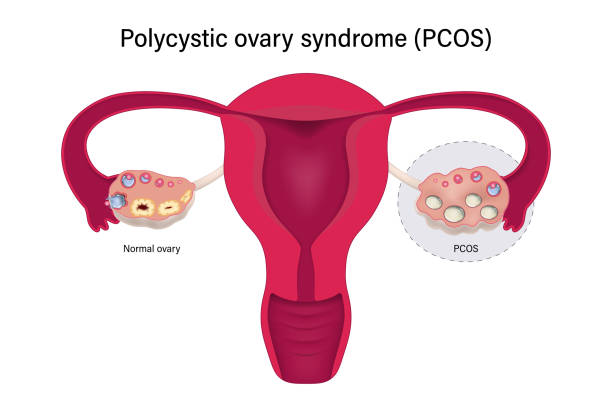
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting millions of women worldwide. It can cause irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, infertility, and other health complications. While there is no cure for PCOS, effective management through medical treatment and lifestyle changes can help reduce symptoms and improve overall health. This guide explores PCOS symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle modifications to help manage the condition effectively.
1. Understanding PCOS and Its Symptoms
PCOS is primarily caused by hormonal imbalances, particularly excess androgens (male hormones) and insulin resistance. Common symptoms include:
- Irregular Periods: Infrequent, prolonged, or missed menstrual cycles.
- Excess Hair Growth: Known as hirsutism, excessive facial and body hair can develop due to high androgen levels.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Hormonal imbalances contribute to persistent acne and increased skin oiliness.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS experience difficulty losing weight due to insulin resistance.
- Hair Thinning: Some women notice thinning hair or male-pattern baldness.
- Difficulty Conceiving: PCOS is a leading cause of infertility due to irregular ovulation.
- Cysts on Ovaries: Small fluid-filled sacs may form on the ovaries, visible through ultrasound.
2. Medical Treatment Options
Treatment for PCOS varies based on symptoms and health goals. Common medical interventions include:
- Birth Control Pills: Regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve acne.
- Metformin: A medication that improves insulin sensitivity, helping regulate blood sugar levels and menstrual cycles.
- Clomiphene (Clomid) and Letrozole: Medications used to induce ovulation for women trying to conceive.
- Spironolactone: Reduces excess hair growth and acne by blocking androgens.
- Ovarian Drilling: A surgical procedure to restore ovulation in severe cases.
3. Lifestyle Changes to Manage PCOS

Lifestyle modifications are crucial in managing PCOS effectively. These include:
A. Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet helps regulate blood sugar levels and manage weight. Focus on:
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Whole grains, vegetables, and legumes to prevent insulin spikes.
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, tofu, and beans to support metabolism.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, and olive oil to improve hormone balance.
- Avoiding Processed Sugars: Reducing sugar intake helps control insulin resistance.
B. Regular Exercise
Physical activity plays a significant role in managing PCOS by improving insulin sensitivity and supporting weight loss. Recommended activities include:
- Cardio Exercises: Walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming for at least 30 minutes daily.
- Strength Training: Building muscle helps regulate metabolism and improve insulin function.
- Yoga and Meditation: Reduces stress and promotes hormonal balance.
C. Weight Management
Losing even 5-10% of body weight can significantly improve PCOS symptoms, including menstrual regularity and ovulation.
D. Stress Reduction
Chronic stress worsens hormonal imbalances. Effective stress management techniques include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Helps lower cortisol levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours per night to support hormonal balance.
- Engaging in Hobbies: Activities like reading, painting, or spending time with loved ones reduce stress.
4. Managing Fertility and Pregnancy with PCOS
Women with PCOS can conceive with proper medical and lifestyle interventions. Steps to improve fertility include:
- Tracking Ovulation: Using ovulation predictor kits or basal body temperature charts.
- Fertility Medications: Ovulation-inducing drugs may be prescribed by a doctor.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): In vitro fertilization (IVF) may be an option for some women.
5. Long-Term Health Risks and Prevention
PCOS increases the risk of various health conditions, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Due to insulin resistance.
- Heart Disease: Higher risk of high cholesterol and hypertension.
- Endometrial Cancer: Irregular periods can lead to excessive thickening of the uterine lining.
Preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular medical check-ups, and early intervention can help reduce these risks.
Conclusion
PCOS is a manageable condition with the right combination of medical treatment, diet, exercise, and stress management. Women with PCOS should work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. By making informed lifestyle changes, it is possible to control symptoms, improve fertility, and enhance overall well-being. If you suspect you have PCOS, seek medical guidance to begin your journey toward better health.